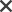A Harris Profile is a way to visualize the strengths and weaknesses of different design concepts.
1. Define and list the requirements that are important for the design concept to be successful.
2. Next to the list of requirements write a 4 point matrix for each concept you want to test. The scale of the matrix is -2, -1, +1, +2.
3. Go through the different concepts and rate each of them based on the requirements. How well do they solve each of the requirements? if they do it very well, mark them as +2, if they are very bad at it mark it as -2.
4. After rating all the concepts, step back and get an overview of the concepts. You can now proceed to filter them based on how well they fit within the different requirements. Make a selection of the most promising ones.
WHEN
After an initial filtering of design concepts and before moving to prototyping a few of them.
WHY
You will need to rate your concepts to decide which ones to develop further.
NOTE!
Use different colors for the positive and negative columns, this helps to quickly visualize the information.
OUTPUT
A short list of concepts to develop and a clear overview on which concepts t the requirements.
Next
Refine and prototype your most promising solutions.
Reference
HARRIS, John S. The Product Profile Chart: A Graphical Means of Appraising and Selecting New Products. 1961./ ROOZENBURG, Norbert FM; EEKELS, Johannes. Product design: fundamentals and methods. Chichester: Wiley, 1995./