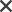A visual method of assessing the current situation and where you want it to be in the future.
1. Draw diagram as shown on the front.
2. Define the level from your perspective.
I. Commodity corner: no collaboration between your organisation & customers, product or service meets customers’ basic specifications, one of many.
II. Providing good products: understand customers’ needs, provide higher quality products.
III. Dedicated service: products & services outperform others in the market, special effort for clients.
IV. Contribute to business issues: understand each customers’ business problems, provide something that few competitors even think about, invest in “merchandising” success.
V. Contribute to organisational issues: account’s “external asset”, understand their long term needs, customers recognise you as key partner.
3. Define the levels from field of players.
4. Evaluate your stage.
Moving up = competition decreases, less sensitivity about price when offering true added value, importance of features decreases because your contribution outweighs anybody’s product and is likely to deliver solutions rather than promises.
WHEN
Long term customer relationships.
WHY
When you have a product in the market.
NOTE!
Get benchmarks to measure relationships and how customers see you and your company.
OUTPUT
Visual assessment of current situation and where you want it to be within three years from now.
Next
Redefine your sales process and strategy.